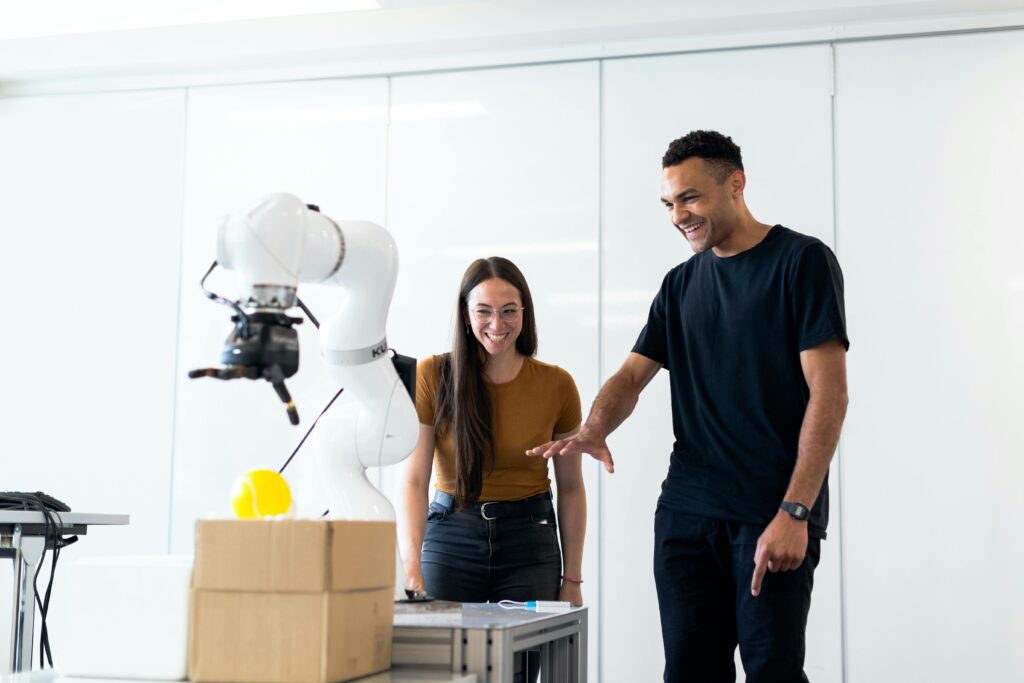
Introduction to 3D Printing Applications
In the ever-evolving world of technology, 3D printing has emerged as a game-changer, revolutionizing industries and pushing the boundaries of what’s possible. As we delve into the realm of additive manufacturing, we uncover a treasure trove of applications that span diverse sectors, each more fascinating than the last. From intricate medical implants to intricate architectural marvels, the potential of 3D printing is limitless, and we’re just scratching the surface.
In this comprehensive exploration, we’ll embark on a journey through 101 mind-blowing 3D printing applications that are transforming the way we live, work, and innovate. Prepare to be amazed as we unveil the incredible versatility of this technology, showcasing how it’s reshaping industries, empowering creativity, and driving sustainable solutions for a better tomorrow.
Additive Manufacturing Applications Across Industries
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has transcended the boundaries of a single industry, permeating a multitude of sectors with its transformative capabilities. From the intricate intricacies of aerospace engineering to the delicate artistry of jewelry design, this revolutionary technology has left an indelible mark on various domains.
As we explore the vast expanse of 3D printing applications, we’ll uncover how diverse industries have embraced this cutting-edge approach, leveraging its precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness to push the boundaries of innovation.
3D Printing in Healthcare: Advancements and Breakthroughs
3D printing is transforming healthcare by enabling personalized treatments, precise medical tools, and breakthrough innovations. From patient-specific implants to bioprinting, the possibilities are redefining how we approach patient care and medical technology.
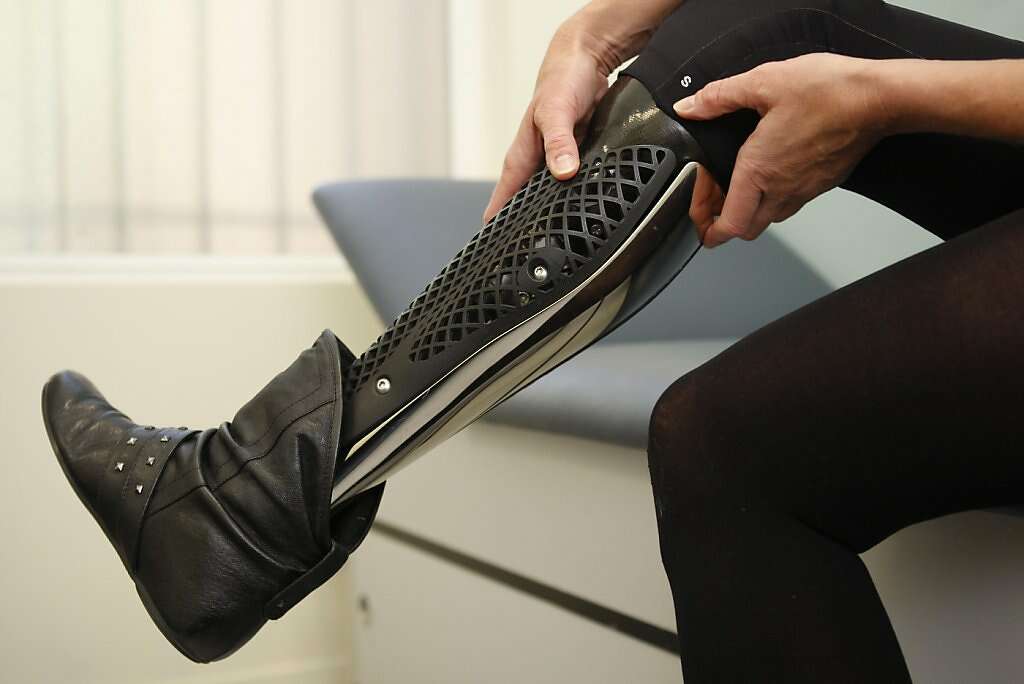

Applications:
- Customized Prosthetics: Tailoring prosthetic limbs to fit individual patients’ anatomy, offering better comfort and mobility than traditional methods.
- Personalized Orthotics: Using 3D scanning and printing to create custom orthotics for patients with unique foot and limb conditions.
- 3D-Printed Surgical Guides: Creating patient-specific surgical guides that help doctors perform complex operations with greater accuracy.
- Bioprinting of Organs: Utilizing 3D printing to fabricate tissues and organs from living cells, with the goal of eventually eliminating organ donor shortages.
- Surgical Training Models: Producing anatomical models for surgeons to practice procedures before performing them on actual patients.
- Custom Dental Implants: Printing dental crowns, bridges, and implants tailored to individual patients for a perfect fit and natural look.
- Hearing Aids Manufacturing: Rapid production of custom-fit hearing aids, made to perfectly fit the ear canal of each user.
- 3D-Printed Bone Implants: Creating bone scaffolds that encourage the natural growth of bone tissue to replace damaged areas.
- 3D-Printed Biodegradable Stents: Producing stents that naturally dissolve over time, reducing the need for additional surgeries.
- Personalized Drug Delivery Systems: Printing custom drug capsules that release medication at controlled rates tailored to individual patient needs.
3D Printing in Aerospace: Revolutionizing the Industry
The aerospace sector is leveraging 3D printing to create lightweight, complex components that enhance performance and reduce manufacturing costs. This technology is reshaping the design and production of aircraft and spacecraft.
Applications:
- Lightweight Aircraft Components: Manufacturing lighter parts that reduce fuel consumption and improve efficiency.
- Complex Engine Parts: Creating intricate engine components that optimize performance and durability.
- Rapid Prototyping for Aircraft Design: Accelerating the design process by allowing for quick iterations of prototypes for testing and validation.
- On-Demand Spare Parts: Printing spare parts on-site, reducing lead times and inventory costs.
- Customized Cabin Interiors: Designing unique and tailored interiors that enhance passenger comfort and experience.
- Functional Testing Models: Producing functional models for aerodynamic testing, allowing engineers to validate designs more efficiently.
- Aerodynamic Design Optimizations: Using 3D printing to create shapes that minimize drag and improve overall aircraft performance.
- Spacecraft Components: Manufacturing parts that can withstand extreme conditions in space, such as high temperatures and radiation.
- Satellite Structures: Designing and producing lightweight structures that reduce the overall weight of satellites for space missions.
- Prototype Drones: Rapidly developing drone prototypes for testing new technologies and designs.
3D Printing in Automotive: Enhancing Design and Production
The automotive industry is harnessing 3D printing to improve design processes, enhance production efficiency, and create customized components. This innovation is reshaping vehicle manufacturing from concept to final product.
Applications:
- Rapid Prototyping for Vehicle Design: Speeding up the design process by quickly producing functional prototypes for testing.
- Customized Interior Components: Printing unique interior elements tailored to individual customer preferences and styles.
- Lightweight Components for Fuel Efficiency: Producing lightweight parts that enhance vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
- Replacement Parts on Demand: Enabling manufacturers to produce spare parts as needed, reducing excess inventory and costs.
- Personalized Grips and Controls: Creating customized grips for steering wheels, shifters, and other controls that enhance driver comfort.
- Complex Engine Parts: Manufacturing intricate engine components that improve efficiency and performance.
- Specialized Tools and Fixtures: Designing and printing tools specific to unique manufacturing processes, enhancing production efficiency.
- Concept Car Models: Rapidly creating detailed concept car models for presentations and marketing.
- Customizable Accessories: Allowing customers to design and order personalized vehicle accessories, such as phone mounts and cup holders.
- Innovative Safety Features: Printing prototypes for new safety technologies to enhance vehicle protection systems.
3D Printed Consumer Goods: Personalization and Customization
3D printing is transforming consumer goods by enabling mass customization and unique designs. This technology empowers individuals to express their styles and preferences through personalized products.
Applications:
- Fashion Accessories: Creating unique jewelry pieces and accessories that cater to individual tastes.
- Personalized Footwear: Designing custom-fit shoes that conform to individual foot shapes for enhanced comfort.
- Home Decor Items: Offering bespoke decorative items like vases and wall art tailored to personal design preferences.
- Custom Toys: Allowing children to design their toys, fostering creativity and engagement in play.
- Unique Gifts: Producing personalized gifts that celebrate special moments, such as custom photo frames or engraved keepsakes.
- Custom Kitchenware: Creating personalized utensils and kitchen gadgets that fit individual cooking styles.
- Personalized Phone Cases: Designing unique phone cases that reflect personal interests and styles.
- Custom Sporting Goods: Manufacturing personalized equipment for sports enthusiasts, such as custom-fit bicycle parts or protective gear.
- Unique Furniture Pieces: Allowing individuals to create customized furniture designs that match their home aesthetics.
- 3D-Printed Fashion Garments: Innovating in fashion design with garments that feature intricate designs and personalization.
3D Printing in Dentistry: Transforming the Field
In dentistry, 3D printing is enhancing patient care through custom dental devices and more efficient treatment processes. This technology is leading to better outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Applications:
- Custom Dental Implants: Printing highly accurate dental implants that fit perfectly to individual patient needs.
- 3D-Printed Orthodontic Appliances: Creating custom braces and aligners that improve treatment effectiveness and comfort.
- Surgical Guides for Implants: Producing precise guides for dental implant surgeries to enhance accuracy.
- Prosthetic Crowns and Bridges: Manufacturing personalized crowns and bridges for a natural fit and appearance.
- Dental Models for Education: Creating anatomical models for dental students to practice and learn about various procedures.
- Customized Mouthguards: Designing custom-fit mouthguards for sports or dental protection.
- 3D-Printed Dentures: Producing dentures that are tailored to individual patients for better comfort and fit.
- Temporary Crowns and Restorations: Rapidly creating temporary crowns during the dental treatment process.
- Orthodontic Study Models: Printing accurate study models for diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Dental Tools and Instruments: Manufacturing specialized tools for dental procedures, enhancing efficiency and precision.
3D Printing for Education: Inspiring Innovation and Creativity
In education, 3D printing is a powerful tool for engaging students and enhancing learning experiences. This technology fosters creativity, collaboration, and hands-on learning.
Applications:
- Interactive Educational Models: Creating 3D models that bring abstract concepts to life, enhancing student engagement.
- STEM Projects: Allowing students to design and print their projects, encouraging problem-solving and critical thinking.
- Customized Learning Materials: Developing personalized learning resources tailored to individual student needs.
- Collaborative Learning Tools: Printing collaborative projects that require teamwork and innovation from students.
- Design Challenges: Organizing competitions where students design and print objects to solve specific problems.
- Prototyping for Inventions: Enabling students to prototype their inventions, fostering entrepreneurship and creativity.
- Educational Kits and Tools: Creating custom kits that aid in teaching complex subjects like biology or physics.
- Cultural Heritage Projects: Allowing students to replicate historical artifacts, deepening their understanding of history.
- Classroom Supplies: Printing unique and customized classroom supplies that enhance the learning environment.
- Hands-On Art Projects: Providing students with the tools to create intricate art projects using 3D printing techniques.
Sustainable 3D Printing: Environmental Benefits and Applications
3D printing is paving the way for sustainable practices by minimizing waste and promoting eco-friendly materials. This technology is integral to creating a greener future.
Applications:
- Reduced Material Waste: Utilizing additive manufacturing to produce objects layer by layer, significantly minimizing waste compared to traditional methods.
- Recycled Materials: Employing recycled plastics and materials to create new products, promoting a circular economy.
- Biodegradable Filaments: Using eco-friendly materials that break down naturally, reducing environmental impact.
- Localized Production: Enabling local manufacturing to minimize transportation emissions and support community economies.
- Sustainable Packaging Solutions: Designing eco-friendly packaging that reduces waste and promotes recycling.
- 3D-Printed Wind Turbines: Creating parts for wind turbines that optimize energy production and sustainability.
- Energy-Efficient Components: Designing lightweight and energy-efficient components for various applications, reducing overall energy consumption.
- Upcycled Products: Transforming waste materials into new, functional products through innovative 3D printing techniques.
- Custom Green Building Materials: Producing materials for sustainable architecture that reduce the carbon footprint of construction.
- Eco-Friendly Home Goods: Printing household items that are both functional and environmentally friendly.
Exploring Different 3D Printing Materials and Their Uses
The variety of materials available for 3D printing significantly expands its application potential. From plastics to metals, each material offers unique benefits for different uses.
Applications:
- PLA Filament: Utilizing biodegradable PLA for a range of applications, including prototyping and consumer goods.
- ABS for Durable Parts: Using ABS for creating sturdy and impact-resistant components.
- Metal Components with DMLS: Producing intricate metal parts for high-performance applications in aerospace and automotive industries.
- Composite Materials: Creating lightweight yet strong parts using carbon fiber-reinforced filaments.
- Ceramic Printing: Producing durable ceramics for dental applications and artistic endeavors.
- Flexible TPU Parts: Printing flexible components like gaskets and wearables using TPU materials.
- Conductive Filaments: Developing electronic devices by integrating conductive materials into 3D-printed components.
- Biomaterials for Medical Use: Utilizing biocompatible materials in the production of medical devices and implants.
- High-Temperature Materials: Creating parts that can withstand extreme temperatures for specialized industrial applications.
- Hybrid Materials: Combining different materials to create products that utilize the strengths of each.
Large Format 3D Printing: Printing on a Grand Scale
Large format 3D printing is revolutionizing how massive structures and components are produced. This approach opens up new possibilities across various industries.
Applications:
- Architectural Models: Creating large-scale models for architects to visualize and present their designs effectively.
- Construction Components: Producing structural elements for buildings that save time and reduce waste.
- Industrial Equipment Parts: Manufacturing large components for machinery, allowing for faster
- Public Art Installations: Creating large sculptures and installations for public spaces that enhance community engagement.
- Custom Furniture Production: Manufacturing oversized furniture pieces tailored to specific design preferences and requirements.
- Vehicle Bodies: Producing large-scale vehicle parts, such as car bodies and components for buses and trucks.
- Event Structures: Printing temporary structures for events and exhibitions, reducing setup time and costs.
- Marine Components: Creating large parts for boats and ships, optimizing weight and performance.
- Modular Housing Elements: Manufacturing components for modular homes that can be quickly assembled on-site.
- Wind Turbine Blades: Producing long and lightweight components for wind turbines, enhancing energy generation efficiency.
- Aviation Parts: Creating large structural components for aircraft, reducing weight while maintaining strength.
- Recreational Vehicle Parts: Printing customized components for RVs, allowing for tailored designs and functionality.
- Temporary Shelters: Manufacturing large temporary structures for disaster relief and housing solutions.
3D Printing in Construction: Revolutionizing Building Practices
3D printing in construction is reshaping how structures are designed and built. This technology offers the potential for faster, more cost-effective, and sustainable construction methods, addressing some of the industry’s most pressing challenges.
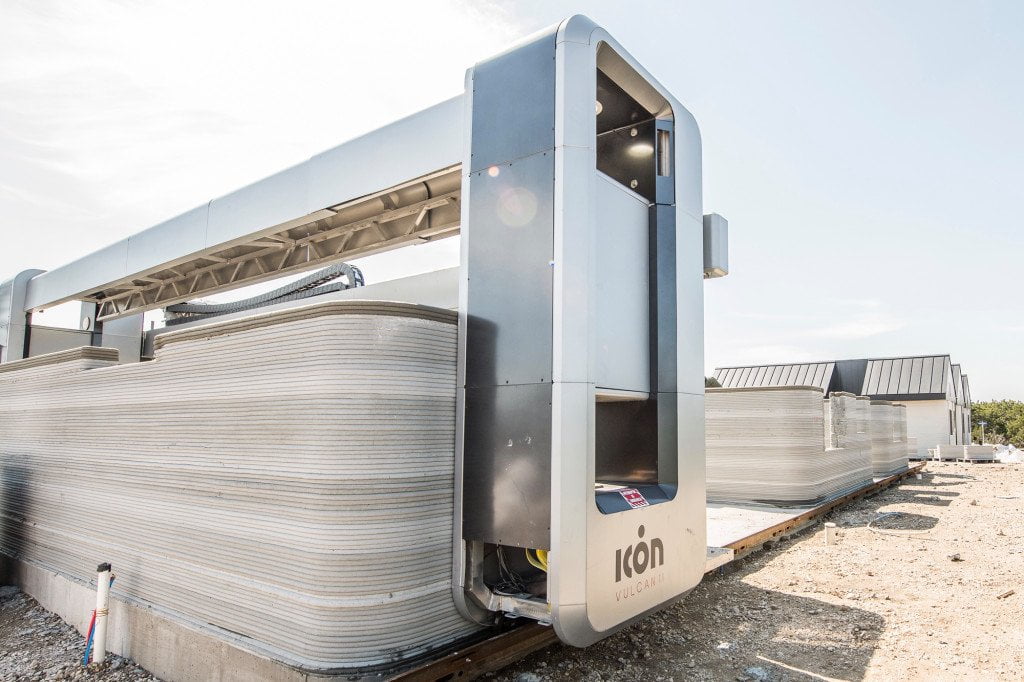

Applications:
- 3D-Printed Homes: Creating entire houses using large-scale 3D printing techniques, significantly reducing construction time and labor costs.
- Custom Structural Elements: Printing unique architectural features and components, allowing for innovative designs that would be challenging with traditional methods.
- Formwork for Concrete: Manufacturing intricate formwork that allows for more complex concrete structures, enhancing design flexibility.
- Building Components: Producing essential building parts, such as walls, roofs, and facades, in a single printing process, streamlining construction.
- On-Site Construction: Utilizing mobile 3D printers to print structures directly on construction sites, minimizing transportation costs and material waste.
- Sustainable Housing Solutions: Developing eco-friendly homes with reduced waste through additive manufacturing techniques that utilize recyclable materials.
- Repair and Restoration: Printing replacement parts or components for the repair and restoration of historic buildings, preserving architectural integrity.
- Community Shelters: Designing and constructing emergency shelters quickly in disaster-stricken areas, offering immediate relief to affected populations.
Conclusion: The Limitless Potential of 3D Printing Applications
As we conclude our exploration of 101 mind-blowing 3D printing applications, it becomes evident that this technology is not just a passing trend but a transformative force reshaping industries and empowering innovation across diverse sectors. From healthcare to aerospace, from consumer goods to construction, the limitless potential of 3D printing is unfolding before our eyes.
The versatility of this technology lies in its ability to create complex geometries, enable mass customization, and produce intricate designs with unparalleled precision. As we continue to push the boundaries of 3D printing, we open doors to new possibilities, sustainable solutions, and groundbreaking advancements that will shape the future of our world.
We’ve linked to a several case studies above that we think exemplify how incredibly 3D printing has been transforming so many industries.
These include within the aerospace industry where GE Aviation utilized 3D printing to create the fuel nozzle for its LEAP engine, selling more than 30,000 fuel nozzles since 2018 using 3D printing!
Within the consumer goods and fashion industry we’re seeing several unique ways that companies are brining 3D printing to you! Adidas had the amazing idea to print the soles of their shoes using 3D printing, calling this line Future 4D and its improvement in performance and range of customizations demonstrate just how wide-reaching 3D printing applications can be!
Embracing 3D printing is not merely about adopting a new technology; it’s about unlocking a world of limitless creativity, efficiency, and innovation. Whether you’re an entrepreneur, designer, engineer, or simply an enthusiast, the time to explore the vast potential of 3D printing and its applications is now!
This post was crafted with the support of AI to provide you with the most accurate, high-quality, and up-to-date content.

